

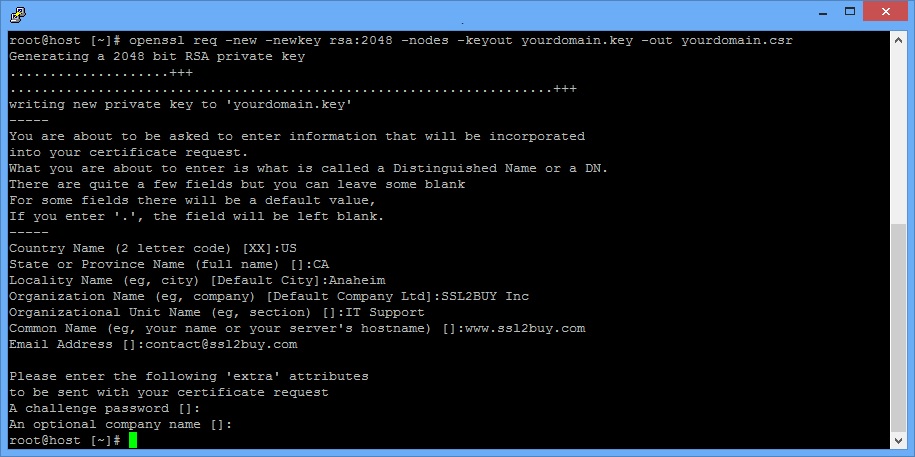
This will create the files localhost.key and localhost.csr in the current folder, using the information in your configuration file. Openssl req -new -key localhost.key -out localhost.csr -config localhost.cnf -extensions v3_req First, create another private key and then generate the CSR using the following commands: Now that you have created your test root certificate, you need to generate a certificate signing request (CSR) and use that to create your server certificate. After you've imported the self-signed root certificate, you're ready to create your server certificate. Make sure you import the certificate into the correct certificate store, and you'll be given a warning prompt about importing the certificate.
#Openssl command install
The simplest way to do this is to open File Explorer, right-click on the file and select Install Certificate to open the Certificate Import Wizard. This certificate must be imported into your Trusted Root Certification Authorities certificate store. The file testCA.crt will be created in the current folder. This tells OpenSSL to create a self-signed root certificate named "SocketTools Test CA" using the configuration file you created, and the private key that was just generated. Openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key testCA.key -sha256 -days 365 -out testCA.crt -config localhost.cnf -extensions v3_ca -subj "/CN=SocketTools Test CA" This will be used with the next command to generate your root certificate: This will create a file named testCA.key that contains the private key. Open a command prompt, change the directory to your folder with the configuration file and generate the private key for the certificate: Creating the Root CertificateĪfter you have created the OpenSSL configuration file, the next step is to create a self-signed root certificate that will be used to sign your localhost test certificate. The common name (CN) for the test certificate will be "localhost" and this is also specified in the section along with the IPv4 and IPv6 localhost addresses.
#Openssl command full
The country code should always be the ISO standard two-letter code (e.g.: US for the United States), and the state/province name and locality should be the full name.
You should change the values in the section to reflect the name of your own organization and location. Copy all of the following text into the file and save it. After you've installed OpenSSL, create a new, empty folder and create a file named localhost.cnf.

The first step to create your test certificate using OpenSSL is to create a configuration file. Then we'll use that certificate to sign a server certificate created for "localhost", the hostname you can use for testing local connections on your development system.
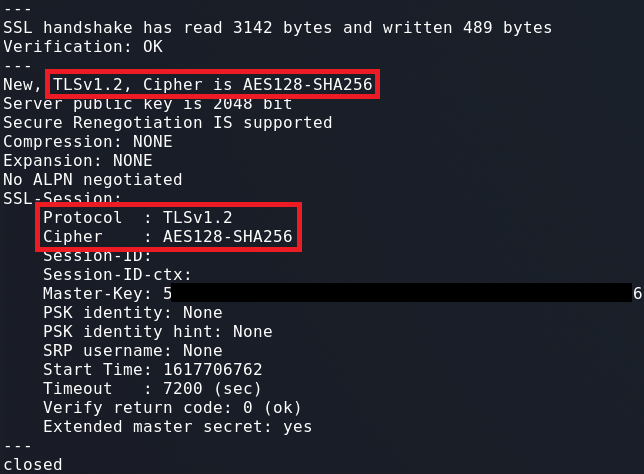
In this article, first we'll create a self-signed root certificate to be installed into the Trusted Root certificate store.
#Openssl command how to
You can download an installation package< that we provide or visit the OpenSSL website for more information on how to obtain other binaries for Windows. You will need to install OpenSSL on your development system to use the commands in this article. This article outlines the steps for creating a test certificate using OpenSSL as an alternative to the MakeCert utility. The OpenSSL toolkit can be used to create self-signed test certificates for server applications, as well as generate certificate signing requests (CSRs) to obtain certificates from Certificate Authorities like DigiCert. Alternatively, you can create your own root and server certificates for testing purposes on your own local network.
#Openssl command windows
These companies have root certificates that are installed as part of the base operating system and will be recognized on all Windows platforms. You can either create a self-signed certificate or purchase one from a Certificate Authority (CA) such as Verisign and Thawte. If the certificate cannot be validated, SocketTools treats this as a soft error and the application decides whether the secure session should be established or the connection terminated. When establishing a secure connection, the SocketTools components will ask the server for its certificate and validate it. NET and ActiveX components, or by using the CreateSecurit圜redentials function in the libraries. SocketTools supports both server and client certificates, by setting the CertificateStore and CertificateName properties in the. There are two types of certificate, those used on the server side, and those which are used by the client to authenticate the session. OpenSSL is an open source toolkit that can be used to create test certificates, as well as generate certificate signing requests (CSRs) which are used to obtain certificates from trusted third-party Certificate Authorities.Ĭertificates are used to establish a level of trust between servers and clients.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
